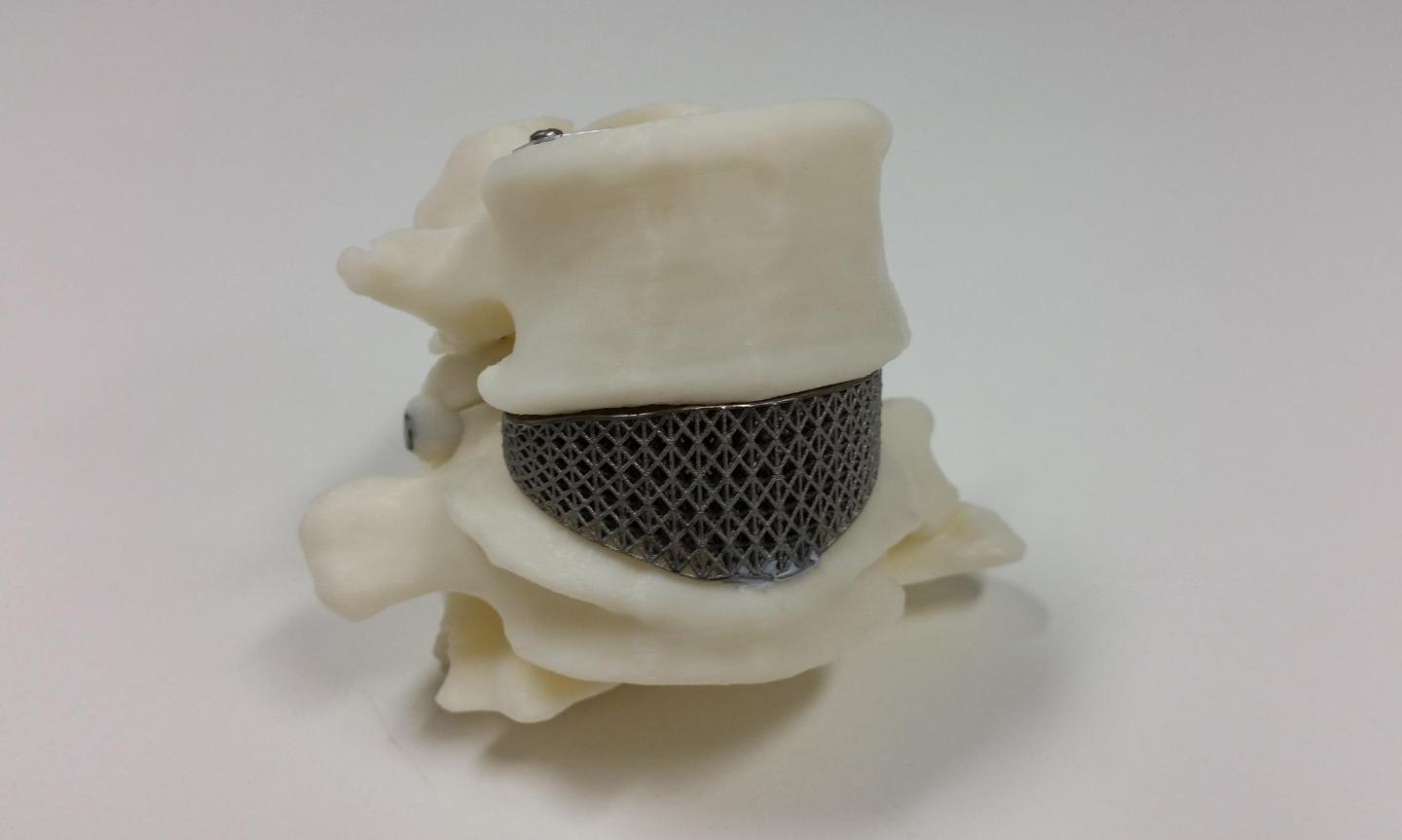
When an abnormal structure of the fifth lumbar vertebra and severe degeneration of the adjacent disc was causing Amanda Gorvin constant lower back pain she was referred to spine surgery specialist Dr Marc Coughlan, at the North Gosford and Prince of Wales Hospitals.
Coughlan’s opinion was that spinal surgery was an option, however due to the unusual shape of Gorvin’s vertebra a standard, off-the-shelf implant would probably only give slight relief.
He then turned to Melbourne medical device specialists, Anatomics who worked with Professor Milan Brandt and his team at RMIT’s Centre for Additive Manufacturing at the Advanced Manufacturing Precinct to design and develop a custom-made titanium spinal implant using 3D printing (or additive manufacturing).
“This revolutionary process allows the implant to be built layer by layer, adding successive layers of material under computer control – as opposed to the subtractive manufacturing techniques of casting, fabrication, stamping and machining,” Brandt said.
“An advantage of 3D printing is that a custom implant can be made of any shape and complex internal architecture for a reasonable cost.”
Specialist teams at Anatomics and RMIT used a CT scan of Gorvin’s spine to create the customised implant while a second medical device supplier, LifeHealthcare, provided additional parts.
In three months since the surgery Gorvin resumed normal activities without any significant pain.
3D printing is proving to be a game changer for manufacturing in the aviation, aerospace, automotive and healthcare industries.
The ability to create unique and complex titanium implants for specific conditions, such as the abnormal shape of Gorvin’s vertebral cage, indicates that additive technology could be used to provide ongoing support for patients with chronic pain.