
From recycling to upcycling: A smarter way of dealing with plastic
Researchers have developed a clean and cost-effective way to upcycle used plastic, transforming it into valuable nanomaterials and high-quality fuel.
Key points
- New tech produces carbon nanotubes and clean liquid fuel from used plastic
- Smart solution for upcycling plastic and agricultural waste simultaneously
- Circular economy approach to help turn two massive waste streams into genuine revenue
Globally only about 20% of waste plastics are recycled. Boosting that figure remains a challenge as recycling plastic cleanly can be expensive and usually produces lower-value products, often making it financially unviable.
The new method from researchers at RMIT University can produce high-value products from plastic – carbon nanotubes and clean liquid fuel – while simultaneously upcycling agricultural and organic waste.
The team’s two-step process, revealed in the Journal of Environmental Management, converts organic waste into a carbon-rich and high-value form of charcoal, then uses this as a catalyst to upcycle the plastic.
Lead researcher Associate Professor Kalpit Shah said upcycling two massive waste streams through one circular economy approach could deliver significant financial and environmental benefits.
“Our method is clean, cost-effective and readily scaleable,” Shah said.
“It’s a smart solution for transforming both used plastic and organic waste – whether tonnes of biomass from a farm or food waste and garden clippings from household green bins.
“We hope this technology could be used in future by local councils and municipal governments to help turn this waste into genuine revenue streams.
“With Australia banning export of waste plastic from next year, it’s vital that we explore sustainable and cost-efficient alternatives beyond recycling.
“Upcycling plastic with home-grown tech would enable us to draw the greatest possible value out of our limited resources and bring us closer towards a true circular economy.”
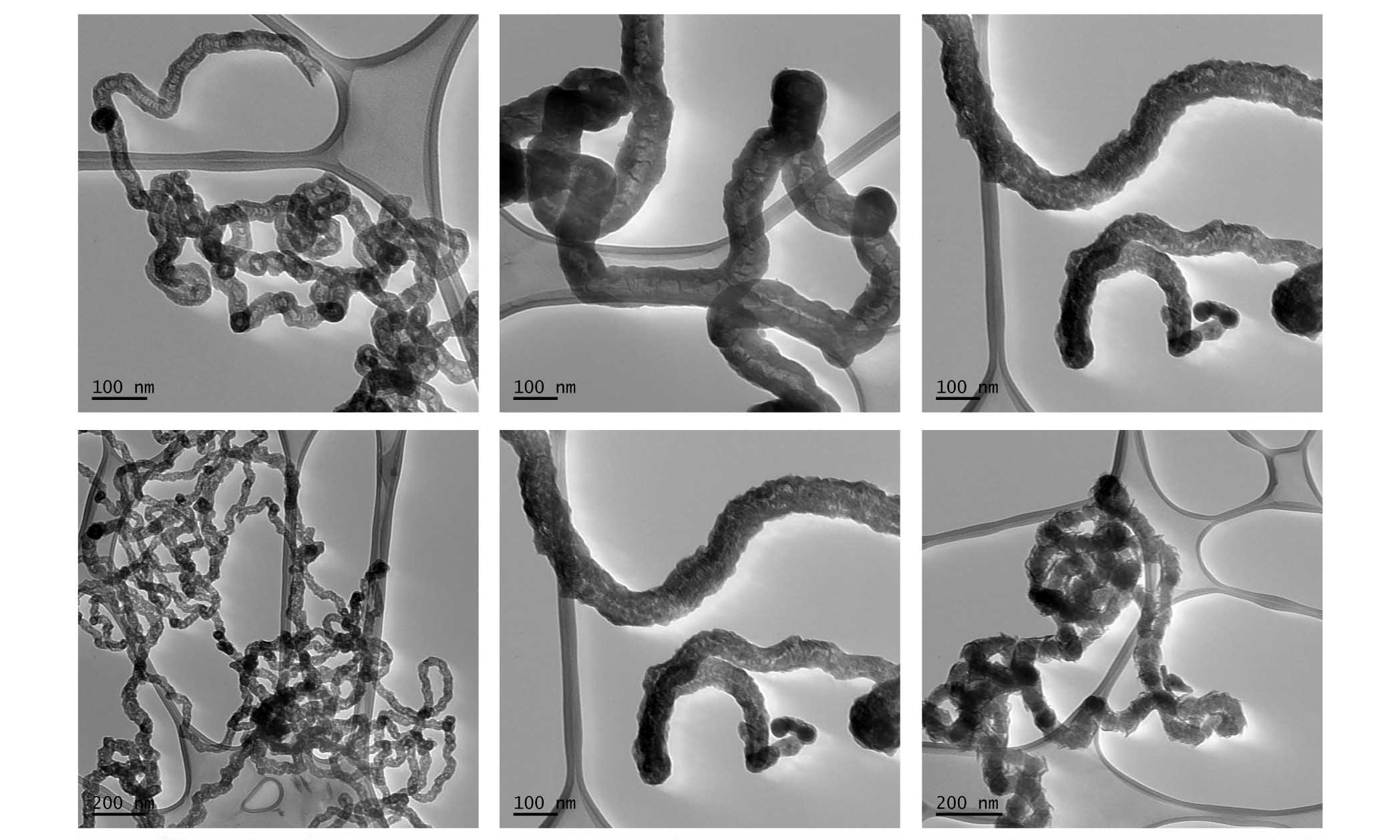 Examples of carbon nanotubes produced with the new approach, at different magnifications.
Examples of carbon nanotubes produced with the new approach, at different magnifications.
Plastic unfantastic
The export of unprocessed single resin/polymer plastics will be banned from July 1, 2022, under new Australian laws designed to phase out export of waste plastics, paper, glass and tyres.
Australia’s national recycling target is for 70% of the country’s plastic packaging to be recycled or composted by 2025, but a recent report found just 9.4% of plastic was recycled in 2017-2018.
Recycling and clean energy is one of six national priorities in the Federal Government's Modern Manufacturing Strategy.
High-value nanomaterials
The new plastic upcycling approach offers a sustainable alternative for the production of carbon nanotubes (CNTs).
These hollow, cylindrical structures have exceptional electronic and mechanical properties, with applications across a broad range of sectors including hydrogen storage, composite materials, electronics, fuel cells and biomedical technologies.
Carbon nanotubes are in growing demand, particularly in aerospace and defence, where they can facilitate the design of lightweight parts. The global market for CNTs has been projected to reach $5.8 billion by 2027.
Turning old into new
The new method starts with converting agricultural or organic waste to biochar – a carbon-rich form of charcoal often used for improving soil health.
The biochar is used to eliminate toxic contaminants – such as Poly-cyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons, known as PAHs - as the waste plastic is broken down into its components of gas and oil.
The process eliminates those contaminants and convert plastics into high-quality liquid fuel.
At the same time, the carbon in the plastic is converted into carbon nanotubes, which coat the biochar.
These nanotubes can be exfoliated for use by various industries or the nano-enhanced biochar can be used directly for environmental remediation and boosting agricultural soils.
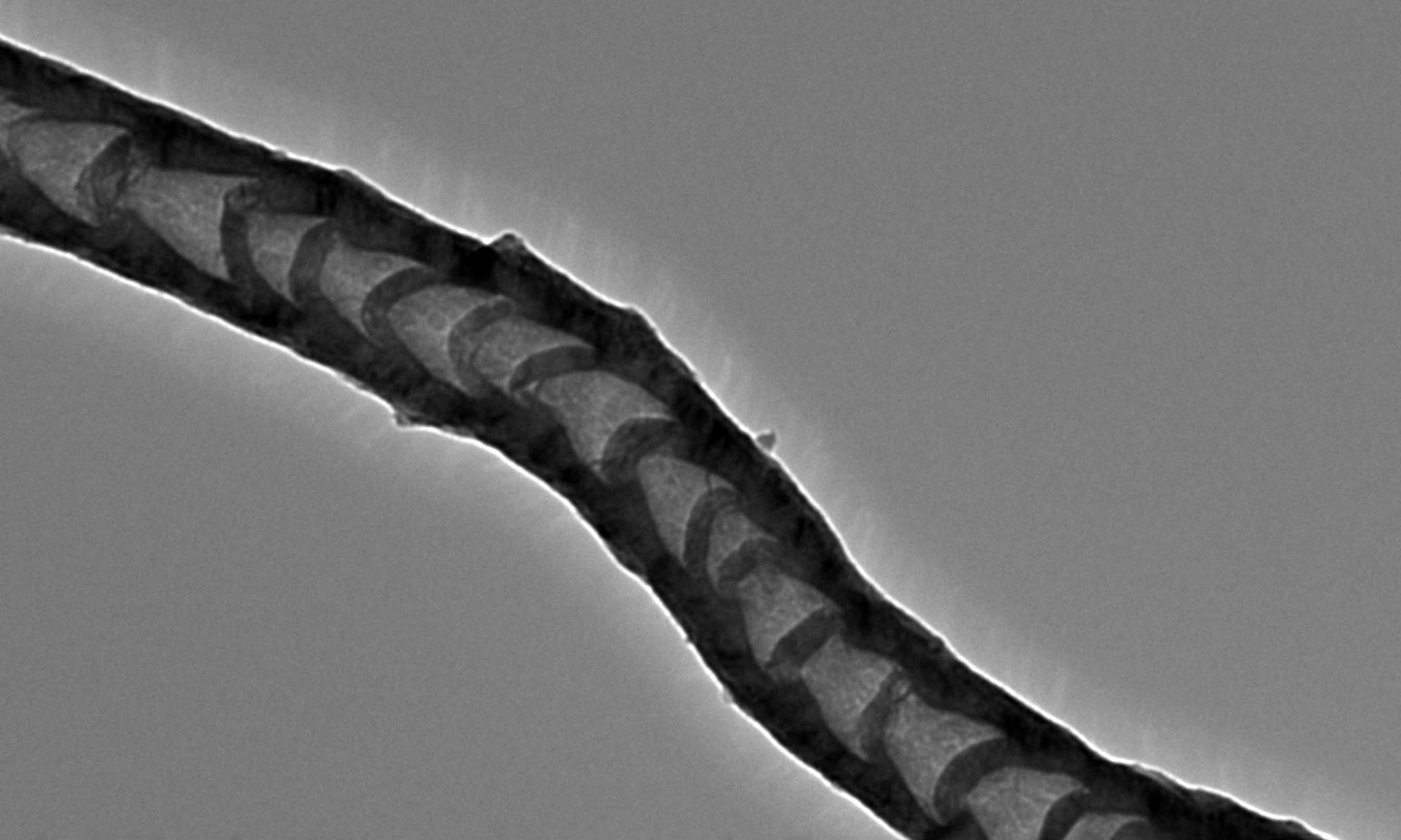 A carbon nanotube created through the new upcycling method. Image magnified 35,000 times.
A carbon nanotube created through the new upcycling method. Image magnified 35,000 times.
The study is the first to use low-cost and widely available biochar as a catalyst for making contaminant-free fuel and carbon nanomaterials from plastic.
Shah, the Deputy Director (Academic) of the ARC Training Centre for Transformation of Australia’s Biosolids Resource at RMIT, said while the study only investigated one type of plastic the approach would be applicable to a range of plastic types.
“We focused on polypropylene as this is widely used in the packaging industry,” he said.
“While we need to do further research to test different plastics, as the quality of the fuel produced will vary, the method we’ve developed is generally suitable for upcycling any polymers - the base ingredients for all plastic.”
Hyper-efficient reactor
The experimental study conducted at lab scale can also be replicated in a new type of hyper-efficient reactor that has been developed and patented by RMIT.
The reactor is based on fluidised bed technology and offers significant improvement in heat and mass transfer, to reduce overall capital and operating costs.
The next steps for the upcycling research will involve detailed computer modelling to optimise the methodology, followed by pilot trials in the reactor.
The team from RMIT’s School of Engineering is keen to collaborate with plastic and waste industries to further the research and investigate other potential applications of the upcycling method.
The research was supported through an Australian Research Council DECRA Fellowship.
‘Conversion of pyrolytic non-condensable gases from polypropylene co-polymer into bamboo-type carbon nanotubes and high-quality oil using biochar as catalyst’, with RMIT co-authors Dr Savankumar Patel, Pobitra Halder, Dr Sazal Kundu, Mojtaba Hedayati Marzbali, Ibrahim Gbolahan Hakeem, Dr Biplob Kumar Pramanik, Dr Ken Chiang and Tejas Patel, is published in the Journal of Environmental Management (DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113791).
Media enquiries: Gosia Kaszubska, +61 417 510 735 or gosia.kaszubska@rmit.edu.au
- Research
- Sustainability
- Nano & Microtechnology
- Science and technology
- Advanced Materials
- Environment
Acknowledgement of Country
RMIT University acknowledges the people of the Woi wurrung and Boon wurrung language groups of the eastern Kulin Nation on whose unceded lands we conduct the business of the University. RMIT University respectfully acknowledges their Ancestors and Elders, past and present. RMIT also acknowledges the Traditional Custodians and their Ancestors of the lands and waters across Australia where we conduct our business - Artwork 'Sentient' by Hollie Johnson, Gunaikurnai and Monero Ngarigo.