In a separate survey we conducted, we found the creation of nude or sexual images was even more prevalent. Of the 4,274 Australians aged 16 to 49 years that we surveyed, 20% said that someone had taken or created a nude or sexual image of them without their consent. Of those surveyed, 9% had experienced threats that a nude or sexual image of them would be shared.
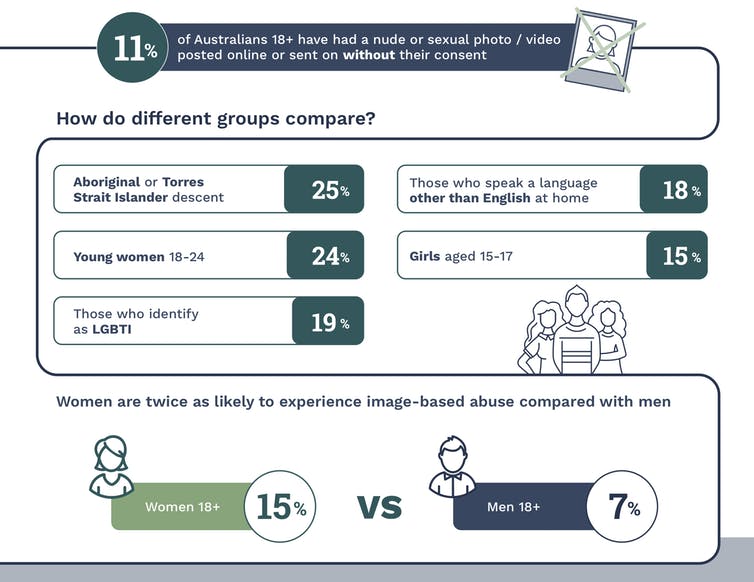
When the creation, distribution and threats to distribute a nude or sexual image were combined, we found that more than one in five (23%) Australians had experienced at least one of these behaviours.
We also asked our survey participants whether they had ever perpetrated image-based sexual abuse. One in 10 reported they had taken, distributed or made threats to distribute a nude or sexual image of another person without that person’s consent. Men (13.7%) were almost twice as likely as women (7.4%) to admit to doing this.
How does IBSA impact victims?
Though the term “revenge porn” implies that the non-consensual sharing of nude or sexual images is based on the spiteful actions of jilted ex-lovers, research suggests the motivations for these behaviours – and the impacts on victims – are far more varied.
For instance, image-based sexual abuse is one way perpetrators of domestic violenceattempt to coercively control a current or former intimate partner. Police and service providers have also described to us how images are used to threaten victims of sexual and domestic violence in order to prevent them from seeking help and reporting to police.
In other cases, nude and sexual images have been used as a form of bullying and harassment, particularly of young people. This can have severe impacts on a victim’s mental well-being, sometimes resulting in self-harm.
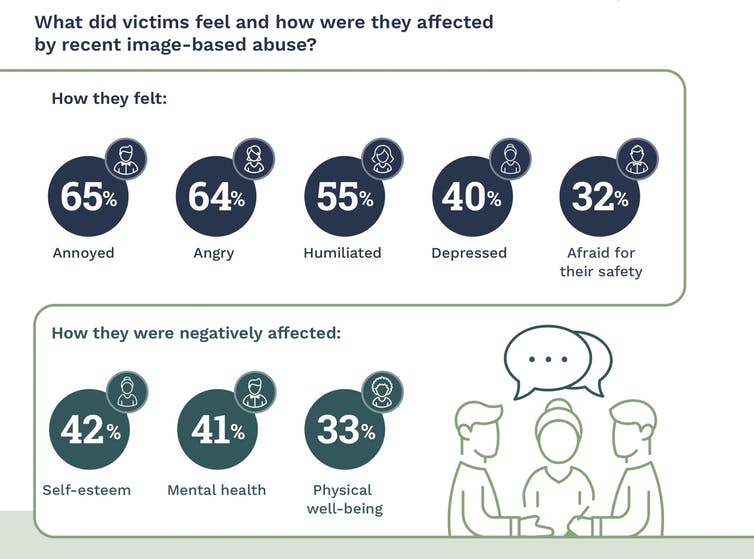
Many victims also experience high levels of psychological and emotional distress. In our study, we found approximately one in three people who experienced IBSA felt fearful for their safety – an indicator of potential stalking or intimate partner abuse being linked to the sharing of images online.