Provide compassionate care and support across diverse healthcare settings, making a meaningful impact on patients' lives.
Nurses are the backbone of the healthcare system, providing essential support, compassion, and expertise to patients and their families. In Australia, the demand for skilled nurses is ever-growing, offering a rewarding career path that combines clinical knowledge with the human touch. Whether you're interested in working in hospitals, community health, or specialised fields, becoming a nurse allows you to make a real difference every day.
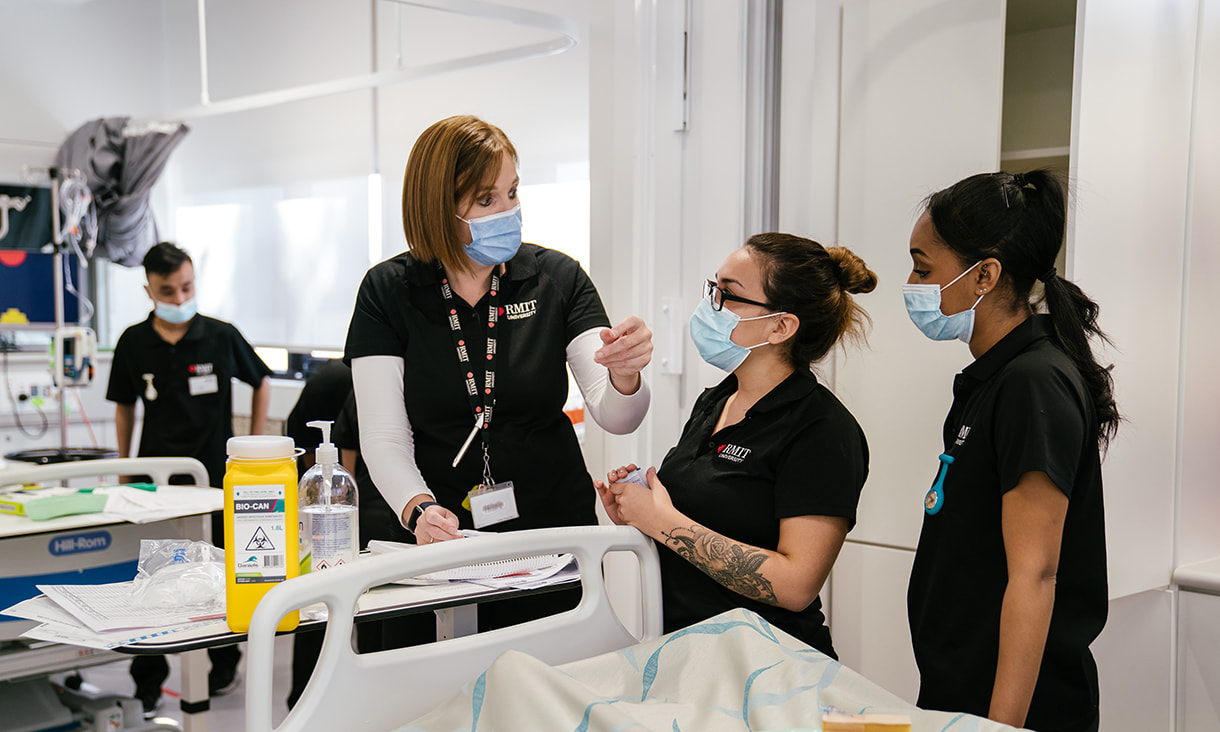

Becoming a nurse
In Australia there are two main types of nurses: a Registered Nurse (RN) and an Enrolled Nurse (EN).
To become a Registered Nurse in Australia, you must successfully complete a Bachelor of Nursing degree accredited by the Australia Nursing and Midwifery Accreditation Council (ANMAC).
To become an Enrolled Nurse in Australia, you must successfully complete a Diploma of Nursing.
Before you begin your course you must show evidence of a completed adult vaccination program and receive a Working With Children Check and a National Police Check. These checks will need to be current throughout your entire course.
Apply for a nursing course
No courses match your current filters
Try adjusting them or reset all filters to see more options
Diploma of Nursing
-
February, July
-
On campus
-
Melbourne City, Bundoora
-
Full-time 2 years
Master of Mental Health Nursing
-
February, July
-
On campus
-
Melbourne City, Bundoora
-
Full-time 1.5 years, Part-time 3 years
Apply for registration
Upon graduation you must then apply for registration with the Australian Nursing and Midwifery Board of Australia (NMBA) to become an officially Registered or Enrolled Nurse in Australia. When applying for registration, in addition to completing your course, graduates will need to meet all registration standards set by the NMBA. Refer to the NMBA Registration Standards for further information.
What does a nurse do?
A nurse plays a crucial role in the healthcare system by providing patient care, support, and education. Their responsibilities include assessing and monitoring patients' health, administering medications and treatments, and collaborating with doctors and other healthcare professionals to develop and implement care plans. Nurses also offer emotional support to patients and their families, helping them understand medical conditions and treatment options. Whether working in hospitals, clinics, or community settings, nurses are dedicated to promoting health, preventing illness, and ensuring that patients receive the best possible care.
What is the difference between a Registered Nurse and an Enrolled Nurse?
A Registered Nurse has completed a Bachelor of Nursing, which provides comprehensive training in clinical skills, patient care, and medical knowledge. RNs have a broader scope of practice, allowing them to perform complex procedures, make critical decisions, and take on leadership roles within healthcare teams. They are often responsible for developing and managing patient care plans, administering medications, and supervising other nursing staff, including Enrolled Nurses.
An Enrolled Nurse, on the other hand, has completed a Diploma of Nursing, which takes less time than a bachelor's degree. ENs work under the supervision of RNs and other healthcare professionals. Their duties include providing basic patient care, such as monitoring vital signs, assisting with daily activities, and administering medications as directed by an RN. While they have a more limited scope of practice compared to RNs, Enrolled Nurses play an essential role in delivering hands-on care and supporting the overall healthcare team.
Both RNs and ENs are vital to the healthcare system, each bringing their unique skills and expertise to ensure patients receive quality care.
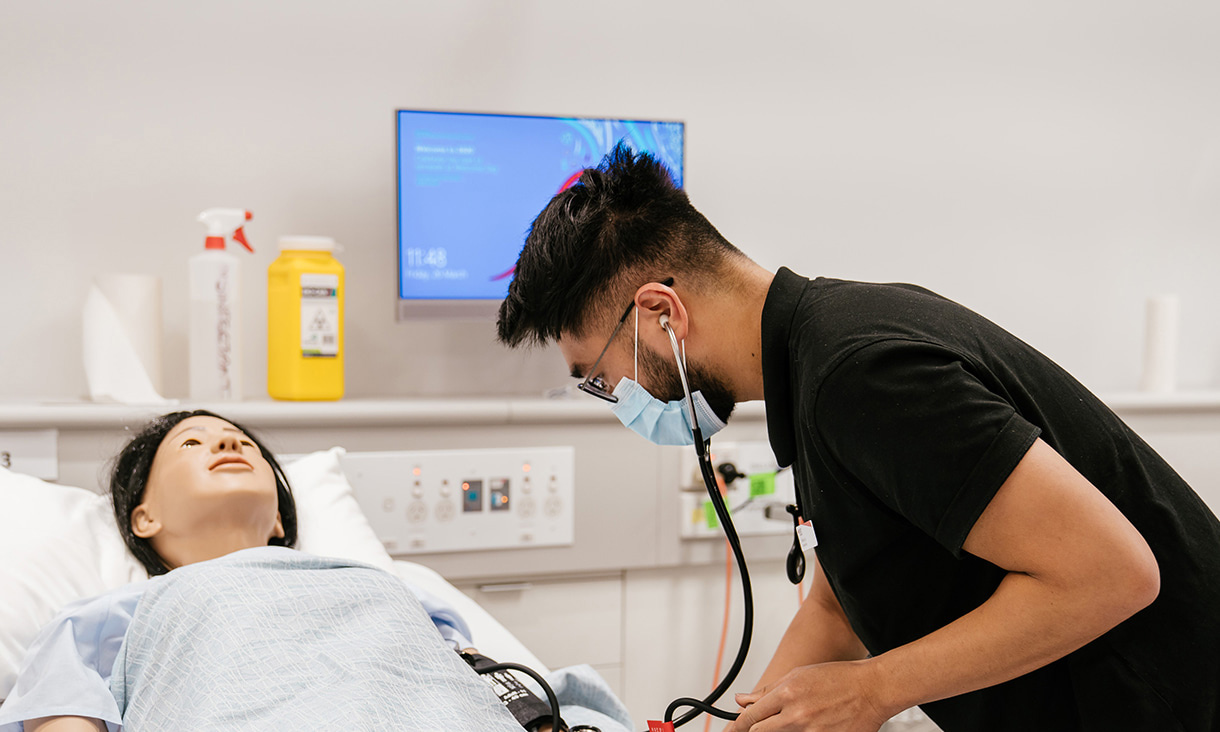
Common tasks, duties, and responsibilities
Nurses perform a wide range of tasks, duties, and responsibilities to ensure the well-being of their patients such as:
- Assess and monitor patient health
- Administer medication and treatment
- Develop and implement patient care plans
- Provide emotional support and education
- Maintain detailed patient records
- Advocate for patients
- Promote health and prevent illness.
Where do nurses work?
Nursing is an essential profession with a high number of employees in Australia and around the world. As a nursing graduate, you have excellent employment prospects in a diverse range of metropolitan, rural, remote, and overseas healthcare settings, including:
- Public and private hospitals
- Community and public health
- Acute care nursing
- Mental health nursing
- Aged-care nursing
- Specialty support services
- Industry and school health nursing
- Healthcare organisations in other countries.
How much do nurses earn?
The median full-time weekly earnings for a registered nurse in Australia is $2,156* and $1,618* per week for an enrolled nurse.
*Source: www.jobsandskills.gov.au 2023
Learn more about your nursing study options
Whether you're a Year 12 student weighing up your options or thinking about switching careers, RMIT's nursing courses provide a comprehensive and industry-focused education that can help you succeed as a nurse in Australia.
Have more questions?
Our friendly staff at Study@RMIT are available five days a week to assist you.


