Kai Rui Wang
Risks of leakage and contamination are incurred by the corrosion of buried steel water pipelines, which cause health and safety hazards to the communities that potable water is delivered to. As much of the corrosion originates from the outer pipe surface, monitoring soil-to-steel interactions is crucial to understanding the physical and chemical mechanisms that cause corrosion. It was found that semi-solid agar could be a good analogue for simulating clay-based soil conditions for corrosion testing; however, a more systematic study needs to be carried out to investigate the metal-bacteria-environment interactions present in microbiologically influenced corrosion situations. Detailed studies are currently being performed to analyse such interactions in the novel semi-solid agar system. The system as an analogue of soil, if validated, would allow significant advancements to laboratory-based research of corrosion in a soil environment, thus allowing the scientific community to better combat MIC for pipelines buried underground.
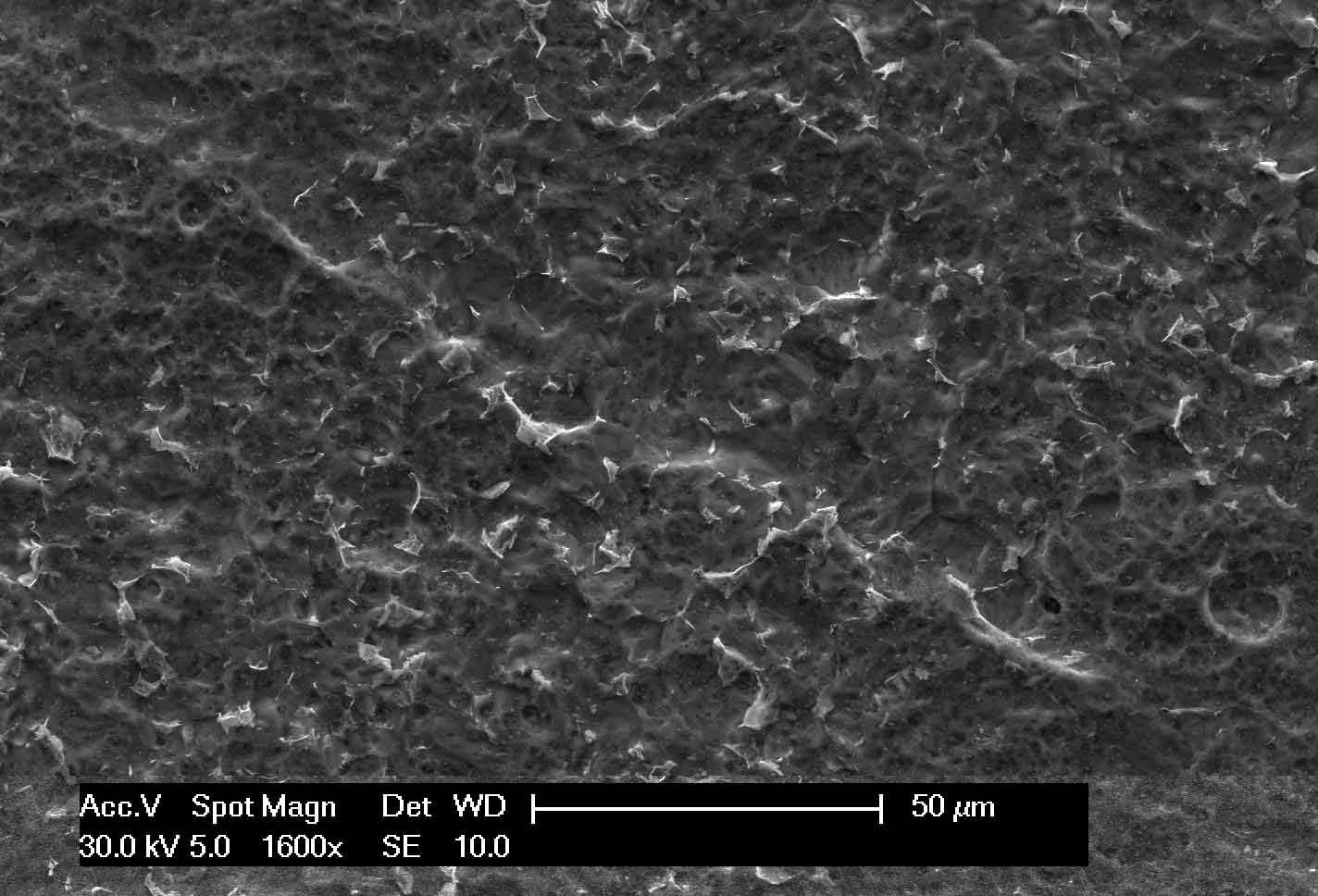 Figure 1: SEM micrograph of HA1 steel after 5.5 h exposure in a semi-solid agar medium
Figure 1: SEM micrograph of HA1 steel after 5.5 h exposure in a semi-solid agar medium
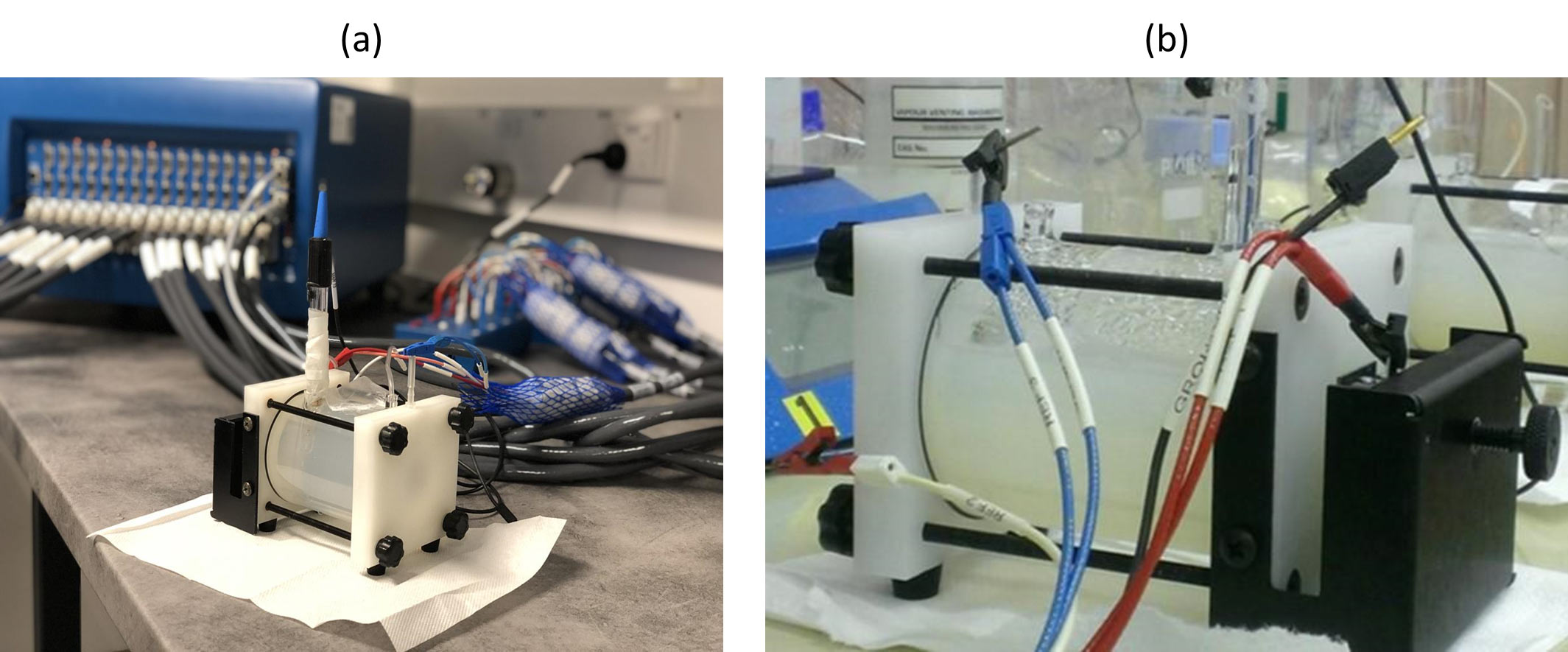 Figure 2: (a) Three-electrode corrosion cell and potentiostat for electrochemical corrosion studies, and (b) close-up view of cell chamber
Figure 2: (a) Three-electrode corrosion cell and potentiostat for electrochemical corrosion studies, and (b) close-up view of cell chamber
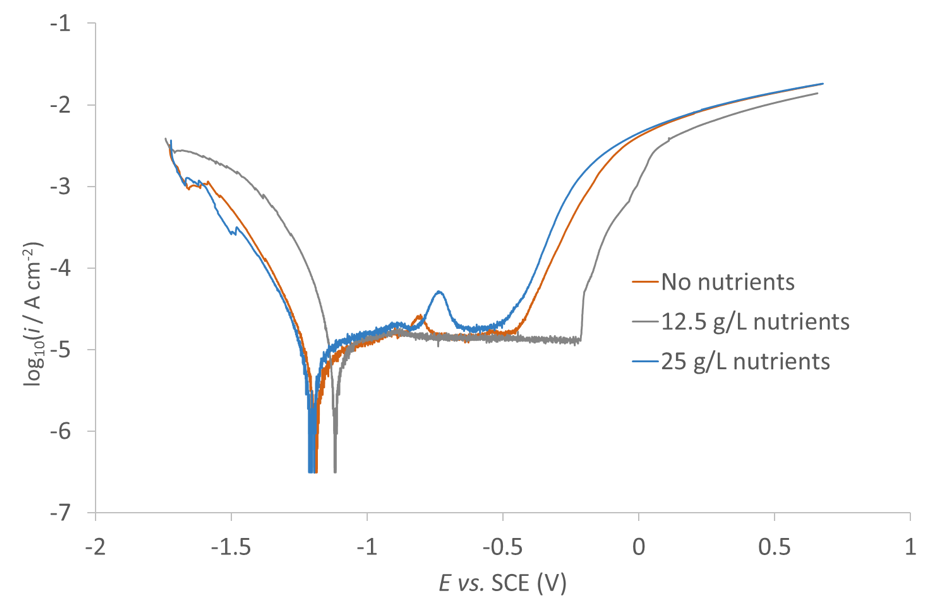 Figure 3: Potentiodynamic polarisation curves of steel coupons in contact with 4 g/L semi-solid agar and nutrients
Figure 3: Potentiodynamic polarisation curves of steel coupons in contact with 4 g/L semi-solid agar and nutrients
Project Publications
- K. Wang, A. Spark, I. Cole, and L. Ward (2019). ‘Effects of electrochemical techniques on carbon steel in agar’, Corrosion & Prevention; 23-27 November 2019, Melbourne, Australia. Paper ID 45. p 1-11.
- A Spark, K. Wang, I. Cole, D. Law, and L. Ward (2020). ‘Microbiologically influenced corrosion: a review of the studies conducted on buried pipelines’, Corrosion Reviews, 38(3), 231-262. DOI: 10.1515/corrrev-2019-0108.

Corrosion and Inhibition
Corrosion inhibitors, corrosion of steel pipes in a soil environment, photocatalysts for CO2 hydrogenation, nano-sensing, optical sensing.